

Mechanically, they are hard like diamond. While diamond is a good insulator, both silicon and germanium are semiconductors (i.e., metalloids).
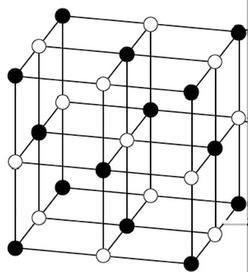
The two elements right under carbon (silicon and germanium) in the periodic table also have the diamond structure (recall that these elements cannot make double bonds to themselves easily, so there is no graphite allotrope for Si or Ge). In diamond, there are four nearest neighbors situated at the vertices of a tetrahedron, and so there is a single bond to each one. In graphite, each carbon has three nearest neighbors, and so there are two single bonds and one double bond. In each one, the valence of carbon atoms is exactly satisfied by making four electron pair bonds to neighboring atoms. Starting at the top, the element carbon has two stable allotropes - graphite and diamond. The carbon group nicely illustrates the transition. This means that as we go down a group in the p-block (let's say, group IVA, the carbon group, or group VA, the nitrogen group), the properties of the elements gradually change from nonmetals to metalloids to metals. Remember where we find the metallic elements in the periodic table - everywhere except the upper right corner. Periodic trends in structure and metallic behavior Body- or face-centered structures fill space more efficiently and more common.
The simple square packing (above) upon which the simple cubic structure is based is inefficient and thus rare among metallic crystal structures. This is the highest volume fraction that can be filled with a lattice of equal spheres.Ītoms in metallic crystals have a tendency to pack in dense arrangments that fill space efficiently. In both cases, it can be shown that the spheres fill 74% of the volume of the lattice. Each atom also has six more nearest neighbors from layers above and below. In the hcp and ccp structures, the atoms pack like stacked cannonballs or billiard balls, in layers with a six-coordinate arrangement. In the bcc structure, the nearest neighbors are at the corners of a cube surrounding the metal atom in the center. We can contrast this with the low coordination numbers (i.e., low valences - like 2 for O, 3 for N, or 4 for C) found in nonmetals. In all three structures the coordination number of the metal atoms (i.e., the number of equidistant nearest neighbors) is rather high: 8 for bcc, and 12 for hcp and ccp. Most metals and alloys crystallize in one of three very common structures: body-centered cubic (bcc), hexagonal close packed (hcp), or cubic close packed (ccp, also called face centered cubic, fcc). These Crystals form double pyramids and prisms.\) Though being square base in its crystal structure, it's height will be longer than the axis. T he tetragonal system has 3 axes which all meet at 90 degrees. Tetragonal: This type is similar to cubic structure however they are longer on axis than the other.In Lattices group of crystals, the researchers have defined 7 different crystalline shapes or structures for identification of crystals which are here below:. 1-Shape of Crystals or Crystals Grouped by Lattices Let us first discuss crystals grouped by Lattices. Crystals by Shape or grouped by Lattices.It is this very specific shape and arrangements of atoms, ions and molecules which gives the minerals and Gemstones, a particular shape or Structure physically.įollowing crystal structures of gemstones and minerals have been defined by the scientists and the researchers. A crystal structure, basically, is a specific form of a gemstone or a mineral, in which there presence a specific arrangements of ions, molecules, atoms inside. What are types of Crystal Structure and how crystals are formed? What is crystal structure definition? This is actually the question, the answer of which will help you in the identification of Gemstones and minerals. What are types of Crystal Structure and how crystals are formed?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
